Multi-crop Passport Descriptors
The Multi-crop Passport Descriptors (MCPD), are a set of standard descriptors for exchange of accession passport data. These fields constitute the minimum set of descriptors that should be used to document accession passport data. MCPD standard is not specific to any crop, so it can be applied to all kinds of plant collections.
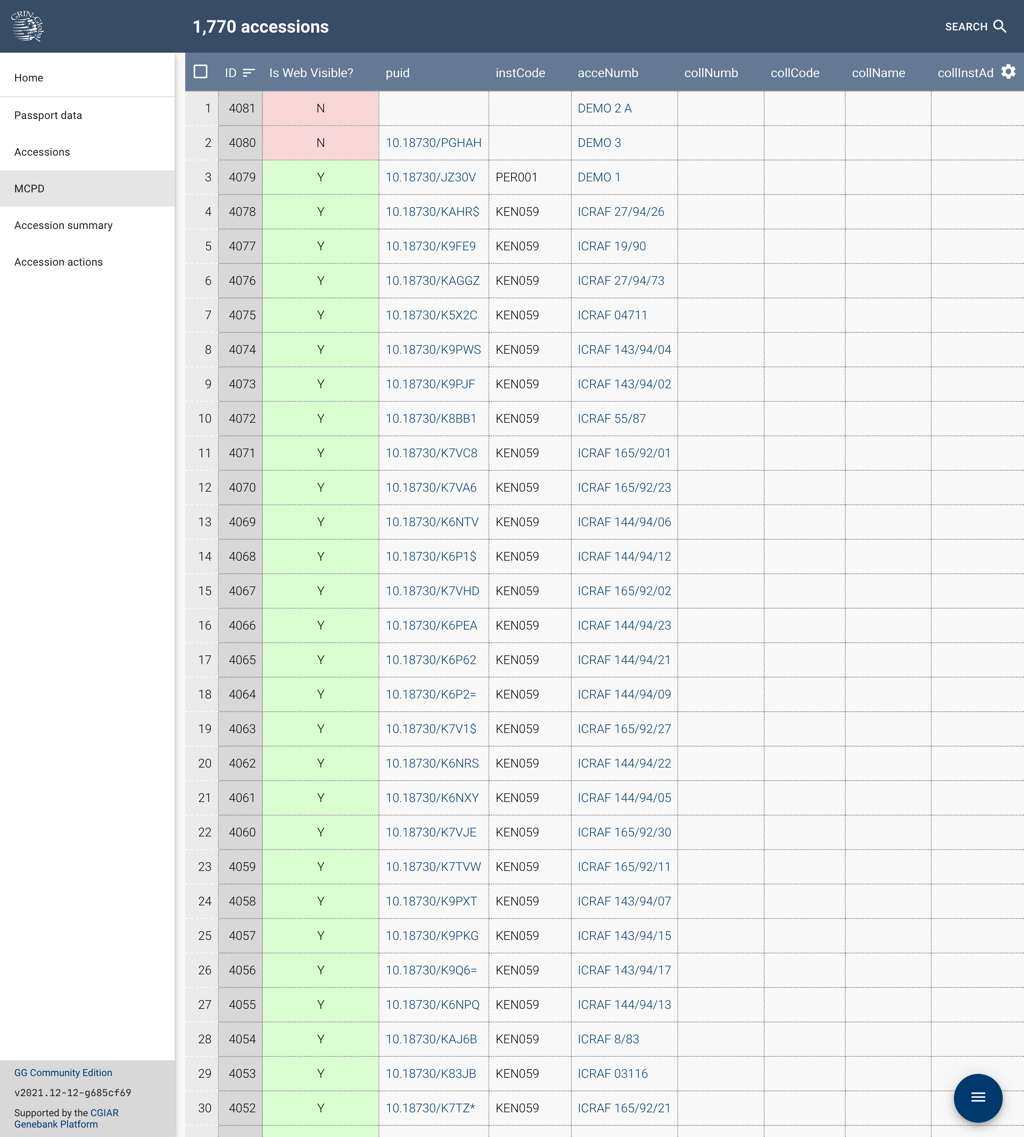
With MCPD being a simple exchange format, multiple values can be recorded in a single spreadsheet cell when separated by ;.
Only a few descriptors allow for multiple values!
GGCE takes care of correctly formatting and translating your accession data to MCPD, but this requires that the information is recorded in the right places!
Accession passport data is recorded with a lot of detail in GGCE. Accession contains the core data about a specific accession in your collection (identifier, acquisition date, level of improvement, etc.).
Accession Names capture different names for the accession, such as the name used by the farmer, name of the variety, or the identifier used by the breeding program. Each name is managed separately to allow for fine-grained identification.
Accession Sources document the history of who collected or bred the material and, if applicable, the organization from which you obtained it.
This document describes how MCPD is generated by GGCE and where to store data so that it shows up under the correct MCPD descriptors based on the three primary areas: Management descriptors, Taxonomic descriptors and information about the Source of the material.
Accessing passport data in MCPD
The MCPD display is an extract of data about each accession in GGCE and its elements are not direclty modifiable.
Upload to Genesys is described in Publishing in Genesys. Download MCPD will produce an Excel file with passport data of the accessions that match the filters.
Management descriptors
The following MCPD descriptors capture the information every genebank knows about each of the accessions in their collection.
PUID Persistent Unique Identifier
The Secretariat of the International Treaty on PGRFA is facilitating the assignment of a persistent unique identifier (PUID), in the form of a DOI, to PGRFA at the accession level.
The DOI can be recorded with each individual accession.
Accession details: Digital Object Identifier field Use the accession form to update the DOI field, labeled as Digital Object Identifier.
GGCE integrates directly with the Treaty's DOI Registration Service and can automatically obtain DOIs for accessions and reupload updated passport data on demand.
INSTCODE Institute Code
FAO WIEWS code of the institute where the accession is maintained. The codes consist of the 3-letter ISO 3166 country code of the country where the institute is located plus a number (e.g. COL001). For institutes, the codes from FAO WIEWS should be used. The current set of Institute Codes is available from the FAO WIEWS site. For those institutes not yet having an FAO Code, or for those with 'obsolete' codes, see ‘Common formatting rules (v)' in the MCPD publication.
Each accession in GGCE is assigned to a Maintenance Site.
The Institute Code of the accession is therefore sourced from the accession's Maintenance Site and the FAO Institute Code it declares.
Admin > Sites: FAO Institute Number field
ACCENUMB Accession Number
This number serves as a unique identifier for accessions within a genebank, and is assigned when a sample is entered into the genebank collection (e.g. PI 113869).
Accession Number is composed of three fields in GGCE: a prefix, number and suffix. The actual formatting of the Accession Number is configurable and allows for zero-padded formats (e.g. VI0000123) and different separators (e.g. a space as in “PI 12345” or a dash as in “TMe-419”).
Accession form: Accession -Prefix, -Number and -Suffix fields
The formatting is a system-wide setting and must be configured by the system administrator.
ACCENAME Accession Name
Either a registered or other formal designation given to the accession. First letter uppercase. Multiple names separated with semicolons without space. For example: Rheinische Vorgebirgstrauben;Emma;Avlon
An accession can have multiple Accession Names. Ideally this is the name used by the farmer, name of the variety, or the identifier used by the breeding program.
Accession > Accession Names list
The name with the highest priority (i.e. lowest rank number) is reported as the MCPD Accession Name.
You can map any of the accession name types (code value group ACCESSION_NAME_TYPE) by giving it the MCPD translation ACCENAME. Otherwise the name with the highest priority will be used.
ACQDATE Acquisition Date [YYYYMMDD]
Date on which the accession entered the collection where YYYY is the year, MM is the month and DD is the day. Missing data (MM or DD) should be indicated with hyphens or “00” (double zero).
The acquisition date is stored as an Initial Received Date on the Accession form.
Accession form > Initial Received Date field
SAMPSTAT Biological Status of Accession
Accession form > Level of Improvement field
The levels of improvement can be adapted to your needs by updating the IMPROVEMENT_LEVEL Code Group.
The mapping of these terms to the MCPD codes is done by the Administrator, and for each level the corresponding SAMPSTAT code is registered as a translation of your code into the MCPD format in GGCE.
STORAGE Type of Germplasm Storage
GGCE looks for all available and publicly shareable inventories of the accession and collects the Type of germplasm storage of their inventory maintenance policies. This in practice means that different inventory maintenance policies need to be applied to material in LTS compared to MTS.
The mapping of germplasm forms to the MCPD codes is done by the Administrator, and for each level the corresponding STORAGE code is registered as a translation of your code into the MCPD format in GGCE.
MLSSTAT MLS Status of the Accession
The status of an accession with regard to the Multilateral System (MLS) of the International Treaty on PGRFA.
0 – No (Not included)
1 – Yes (Included)
99 – Other (Elaborate in REMARKS section)
Accession form > MLS Status of the Accession field
The mapping of different states to their MCPD counterparts is done by the Administrator, and for each one the corresponding MLSSTAT code is registered as a translation of your code into the MCPD format in GGCE.
OTHERNUMB Other Identifiers Associated with the Accession
GGCE stores all names and identifiers used by other institutes for the accession as Accession Names.
Accession > Accession Names: Name field
GGCE aggregates all names except for the names already used for other MCPD descriptors: Accession Name, Collecting Number and Donor Number. Those are excluded from OTHERNUMB.
DUPLSITE Location of Safety Duplicates
FAO WIEWS code of the institute(s) where a safety duplicate of the accession is maintained.
Accession form: Backup Location 1 and Backup Location 2 fields
The FAO Institute Numbers are stored in the FAO Institute Code field of the Site record.
DUPLINSTNAME Institute Maintaining the Safety Duplicate
Name of the institute(s) where a safety duplicate of the accession is maintained.
Backup Location 1 and Backup Location 2 fields
The Site’s Long Name is used as the name of the institute.
REMARKS Remarks
The Remarks field is used to add notes.
The Remarks field is not used by GGCE.
Taxonomic data
GGCE encourages the use of GRIN Taxonomy to ensure accurate identification of accession species. The MCPD descriptors related to taxonomy of each accession are sourced from accession's species record.
GENUS Genus
Genus name for taxon. Initial uppercase letter required.
SPECIES Species
Specific epithet portion of the scientific name in lowercase letters. Following abbreviation is allowed: ‘sp.'
Both genus and species are stored in the Taxon field on the Accession form.
Accession form: Taxon field
SPAUTHOR Species Authority
Provide the authority for the species name.
SUBTAXA Subtaxa
Subtaxa can be used to store any additional taxonomic identifier. Following abbreviations are allowed: ��“subsp.” (for subspecies); “convar.” (for convariety); “var.” (for variety); “f.” (for form).
SUBTAUTHOR Subtaxa Authority
Provide the subtaxa authority at the most detailed taxonomic level.
The Subtaxa field should specify the most detailed taxonomic level.
The name author is defined with each species record and is reported as Species Authority or Subtaxa Authority.
CROPNAME Common Crop Name
Name of the crop in colloquial language, preferably English (i.e. ‘malting barley’, ‘cauliflower’, or ‘white cabbage’).
The crop name is determined from the association between the taxon and the Crop. Each species name in your collection should be linked with the appropriate Crop record.
Crops > Crop > Species
About the source of material
For each accession, the information about the history of how it came to your collection is stored in Accession Source records. There are three types of Accession Source: COLLECTED, DEVELOPED and DONATED.
If the material was obtained from another organization, you store that information as a source of type DONATED. You cannot donate the material to yourself – when the material came to the genebank from the breeding program in the same institute, use DEVELOPED; if collected by another program or unit of your organization, then use COLLECTED instead.
The types COLLECTED and DEVELOPED are mutually exclusive and only one should be registered.
If the material was originally collected from in situ conditions by you or another organization (e.g. the donor institute), the information is stored as the source of type COLLECTED.
If the material in its current form is a result of breeding, the information about the breeder is stored as a source of type DEVELOPED.
Each of the Accession Sources should be linked with relevant Cooperators, be it donors, collectors, or breeders. You can use institutional or individual Cooperators. The Cooperator address book is used to store information about cooperators (individuals or organizations).
Accessions obtained from another organization
In the event that you sourced the material from another genebank and did not collect it yourself or develop it in your breeding program, then you should add the records about the donor of the material to GGCE as the Accession Source of type DONATED.
DONORCODE Donor Institute Code
FAO WIEWS code of the institute from which you sourced the accession.
The FAO Institute Code of the Cooperator of Accession Source of type DONATED.
DONORNAME Donor Institute Name
The name of the institute from which you sourced the material.
The name of the institute is an optional descriptor when the FAO Institute Code is not known.
Accession > Accession Source Cooperators
Cooperators form: Organization Name field
DONORNUMBER Donor Number
The identifier used for this accession at the donor institute.
The germplasm number as used by the donor is one of the other names or identifiers for this accession, and is recorded as an accession name of the category Donor identifier DONOR.
Accession > Accession Names: Name field of type Donor identifier
You can map any of the accession name types (code value group ACCESSION_NAME_TYPE) by giving it the MCPD translation DONORNUMB.
Material collected from in situ conditions
Regardless of the material being donated, if the material was originally collected from in situ conditions you should record the relevant information as the Accession Source of type COLLECTED, and this must also be flagged as Is Origin.
If the accession is a result of breeding, then there was no collecting event and therefore the collecting information is not applicable. Calculation of Passport Data Completeness Index (PDCI) takes this into account and considers any collecting information for breeding lines to be an error.
COLLNUMB Collecting Number
Original identifier assigned by the collector(s) of the sample, normally composed of the name or initials of the collector(s) followed by a number (e.g. “FM9909”). This identifier is essential for identifying duplicates held in different collections.
The germplasm number assigned to the collected sample by the collector is one of the other names or identifiers for this accession, and is recorded as an accession name of the category Collector identifier COLLECTOR.
Accession > Accession Names: Name field of type Collector identifier
You can map any of the accession name types (code value group ACCESSION_NAME_TYPE) by giving it the MCPD translation COLLNUMB.
COLLCODE Collecting Institute Code
FAO WIEWS code of the institute collecting the sample. If the holding institute has collected the material, the collecting institute code (COLLCODE) should be the same as the holding institute code (INSTCODE). Follows INSTCODE standard.
The information about the collectors is stored as Cooperator records and linked to the Accession Source of type COLLECTED. The FAO Institute Code of the Cooperator is used.
Accession > Accession Source Cooperators
Cooperators form: FAO Institute Code field
COLLNAME Collecting Institute Name
Name of the institute collecting the sample. This descriptor should be used only if COLLCODE cannot be filled because the FAO WIEWS code for this institute is not available.
The name of the collecting institute is an optional descriptor when the FAO Institute Code is not known.
Accession > Accession Source Cooperators
Cooperators form: Organization Name field
COLLINSTADDRESS Collecting Institute Address
Address of the institute collecting the sample. This descriptor should be used only if COLLCODE cannot be filled because the FAO WIEWS code for this institute is not available.
The address of the collecting institute is an optional descriptor when the FAO Institute Code is not known. The address is stored in the Cooperator record.
Accession > Accession Source Cooperators
Cooperators form: Address fields
COLLMISSID Collecting Mission Identifier
Identifier of the collecting mission used by the Collecting Institute (e.g. CIATFOR-052, CN426).
The identifier of the collecting mission is stored under Accession Names as a name with the category Exploration ID EXPLORATION.
You can map any of the accession name types (code value group ACCESSION_NAME_TYPE) by giving it the MCPD translation COLLMISSID.
ORIGCTY Country of Origin
3-letter ISO 3166-1 code of the country in which the sample was originally collected (e.g. landrace, crop wild relative, farmers' variety), bred or selected (breeding lines, GMOs, segregating populations, hybrids, modern cultivars, etc.).
The ISO country code of the Geography of the Accession Source flagged as Is Origin.
Accession > Accession Source > Geography field
COLLSITE Location of Collecting Site
Location information below the country level that describes where the accession was collected.
Location information below the country level is stored in the Accession Source record.
Accession > Accession Source > Formatted Locality field
Geographical Coordinates
For latitude and longitude coordinates, two alternative formats are proposed, but the one reported by the collecting mission should be used.
GGCE stores geographical coordinates in decimal format only. If you need to store the degree formats, you can consider using the relevant Note fields.
DECLATITUDE Latitude of Collecting Site (Decimal Degrees Format)
Latitude expressed in decimal degrees. Positive values are north of the Equator; negative values are south of the Equator (e.g. -44.6975).
Decimal-format latitude is stored in the Accession Source record.
Accession > Accession Source > Latitude field
LATITUDE Latitude of Collecting Site
As GGCE stores all geographical coordinates in decimal format, the MCPD LATITUDE descriptor is not used.
DECLONGITUDE Longitude of Collecting Site (Decimal Degrees Format)
Longitude expressed in decimal degrees. Positive values are East of the Greenwich Meridian; negative values are West of the Greenwich Meridian (e.g. 120.9123).
Decimal-format longitude is stored in the Accession Source record.
Accession > Accession Source > Longitude field
LONGITUDE Longitude of collecting site
As GGCE stores all geographical coordinates in decimal format, the MCPD LONGITUDE descriptor is not used.
COORDUNCERT Coordinate Uncertainty
Uncertainty associated with the coordinates in meters. Leave the value empty if the uncertainty is unknown.
Coordinate Uncertainty is stored in the Accession Source record.
Accession > Accession Source > Coordinate Uncertainty field
COORDDATUM Coordinate Datum
The geodetic datum or spatial reference system upon which the decimal latitude and longitude coordinates are based (WGS84, ETRS89, NAD83). The GPS uses the WGS84 datum.
Georeference Datum is stored in the Accession Source record.
Accession > Accession Source > Georeference Datum field
GEOREFMETH Georeferencing Method
The Georeferencing Method used (GPS, determined from map, gazetteer, or estimated using software. Leave the value empty if the Georeferencing Method is unknown.
Georeferencing Protocol is stored in the Accession Source record.
Accession > Accession Source > Georeferencing Protocol field
ELEVATION Elevation of Collecting Site
Elevation of collecting site expressed in meters above sea level. Negative values are allowed.
Elevation is stored in the Accession Source record.
Accession > Accession Source > Elevation field
COLLDATE Collecting Date of Sample [YYYYMMDD]
Collecting date of the sample, where YYYY is the year, MM is the month, and DD is the day. Missing data (MM or DD) should be indicated with hyphens or “00” (double zero).
The date of the collecting of the sample is stored under Source Date in the Accession Source table.
Accession > Accession Source > Source Date field
COLLSRC Collecting / Acquisition Source
Accession > Accession Source > Source Habitat field
The different habitat types can be adapted to your needs by updating the ACCESSION_SOURCE_HABITAT_TYPE Code Group.
The mapping of these terms to the MCPD codes is done by the Administrator, and for each type you use the corresponding COLLSRC code is registered as a translation of your code to the MCPD format in GGCE.
Breeding material
The descriptors related to the event of collecting of material from in situ conditions are recorded as the Accession Source of type BREEDING. This includes cases where the material was developed by you or your organization.
BREDCODE Breeding Institute Code
FAO WIEWS code of the institute breeding the sample. If the holding institute has collected the material, the breeding institute code (BREDCODE) should be the same as the holding institute code (INSTCODE). Follows INSTCODE standard.
The information about the breeders is stored as Cooperator records and linked to the Accession Source of type BREEDING. The FAO Institute Code of the Cooperator is used as the Breeding Institute Code.
Accession > Accession Source Cooperators
Cooperators form: FAO Institute Code field
BREDNAME Breeding Institute Name
Name of the institute or person who bred the material. This descriptor should be used only if BREDCODE cannot be filled because the FAO WIEWS code for this institute is not available.
Only required when the code of the institute is not known.
Cooperators form: Organization Name field
ANCEST Ancestral Data
Information about pedigree or other description of ancestral information (e.g. parent variety in case of mutant or selection).
Use the Accession Pedigree records.
The description of the first Pedigree record is reported as MCPD Ancestral Data.
Genesys descriptors
CURATION Curation type
The type of curation of an accession in GGCE is mapped to Genesys CURATION descriptor.
Accession form: Curation Type field.
The mapping of germplasm forms to the MCPD codes is done by the Administrator, and each CURATION_TYPE code should be translated to the corresponding MCPD value: FULL, PARTIAL, ARCHIVED or HISTORICAL.
HISTORICAL Historical accessions
The flag determines if the accession is a historical record of an accession that no longer exists in the collection.
Accessions of any Curation Type are flagged as active (not historical) except when the curation type is Historical. When Curation Type is not specified then GGCE takes into account the Status of the accession.
Please use accession's Curation type instead.
Accession form: Accession Status field.
The mapping of germplasm forms to the MCPD codes is done by the Administrator, and each ACCESSION_STATUS code should be translated to false for active accessions and true for historical.
AVAILABILITY Availability for distribution
Genesys allows genebanks to specify if an accession can be requested via Genesys by specifying its availability. Three options are recognized by Genesys:
AVAILABILITY | Notes |
|---|---|
true | Accession is available for distribution and can be requested via Genesys. |
false | Accession exists, but is not available and cannot be requested via Genesys. Genesys will exclude such accessions from requests for material. |
null | Availabilty is not specified, the accession may or may not be available for distribution. Genesys allows users to include such accessions in their request. |
GGCE calculates AVAILABILITY flag by inspecting each accession's inventory:
- Availability is not specified (
null) when none of its inventories have Quantity on hand specified. - Accession is flagged with
truewhen there exists at least one inventory that Is Distributable and Is Available and has Quantity on hand above the distribution threshold. - In all other cases the availability for distribution is set to
false
Mapping your data to MCPD
A few MCPD listed above, for example Biological Status of Accession, are coded descriptors that use a specific vocabulary.
GGCE uses the MCPD language that lets you translate your vocabulary terms to the terms defined in MCPD.
Please translate the following vocabularies to MCPD:
IMPROVEMENT_LEVELto MCPDSAMPSTATSTORAGE_TYPEto MCPDSTORAGEACCESSION_SOURCE_HABITAT_TYPEto MCPDCOLLSRCCURATION_TYPEto Genesys descriptorCURATIONACCESSION_STATUSto Genesys descriptorHISTORICAL
When the terms of these vocabularies are not translated to MCPD, the data will not be included, even if it exists in your GGCE!