Passport data
An accession is a distinct sample of germplasm representing a cultivar, breeding line, or a wild or cultivated population, maintained in a genebank for conservation and use. Its genetic stability is optimally preserved through careful monitoring and multiplication.
The passport data records where the material is coming from, who provided it, what it is, and what it is called. An accession-level record is created immediately when new material arrives in the genebank, either from a collecting mission, from a transfer from another genebank or breeding program. The record is assigned a (temporary) accession identifier and the passport data regarding its provenance, collecting, donation or breeding pedigree is recorded. The passport data of material in genebanks is commonly exchanged following the Multi-Crop Passport Descriptors (MCPD) standard.
Not all material will be accepted into the collection. Regardless, the passport data is never discarded and becomes part of the historical archive of the genebank and allows for checking whether material was already received, accepted or rejected by the genebank in the past.
The information about the physical material of one accession from one or more generations, split into packets and maintained in different storage locations, is recorded as accession inventory. The bulk of the data generated by the genebank is linked to individual physical inventories, not to the accession as a whole.
Accession identifiers
The accession number is the unique identifier given by the genebank to the germplasm. GGCE builds the accession number from its three components: prefix, sequence number and suffix. The concatenation of the three components represents the complete accession number.
The prefix is commonly used to identify the collection where the accession is maintained, for example IRGC at IRRI genebank, PI in USDA NPGS and IG at ICARDA. A special prefix should be used to quickly identify material not yet accepted into the collection (e.g. INTRO or TEMP).
The numeric part of the accession number must be stored in the sequence number field. By separating the numeric part from the prefix, GGCE is able to automatically assign the next available accession number for the selected prefix on demand. The sequence number of an accession must be unique within the prefix group.
Avoid storing the entire accession number in the prefix field, if possible. GGCE manages the sequence number and allows for automatic numbering.
The suffix is commonly used if an accession is split and the parts are then managed independently.
The formatting of the complete accession number based on the three parts is configurable. The sequence number may also be zero padded.
When material enters the genebank, it is given a temporary accession number. When the material passes the acquisition criteria, the proper accession number is assigned: it is given the official prefix and the next available number in sequence. Once the accession number has been assigned, it is strongly advised to not change it or reuse it for a different sample.
In addition to the accession number, a Digital Object Identifier (DOI) can be assigned to an accession. DOIs are guaranteed to be globally unique and they point to a web resource where information about the accession can be found. This identifier is unique and immutable, unlike the accession number which might change.
Passport data
Passport data is implemented with a central record that holds the accession’s unique number in the collection, its scientific name, and a set of status flags. Additional details are organized into categories such as names, source history, pedigree, Intellectual Property Rights and restrictions (IPR), quarantine status, etc.
Accession Source entries record the history of how the material came to the genebank: from the collection of material in situ, or where it was originally developed/bred, how it was transferred from institute to institute before coming to our genebank. The source history is commonly provided with the passport data accompanying the incoming material. One Source record should be flagged as “origin”, signifying that this record’s Geography will be considered as the original provenance of the accession.
Accession Names allow to record the names and identifiers of the material as used by farmers, local communities, collectors, breeders, genebanks and other institutes. These are also commonly included with the passport data of incoming material. Please note that names of persons and organizations do not belong here, instead they are linked with the appropriate Source record.
Access and management of this data is handled in the Passport Data area of GGCE and divided into the following sections:
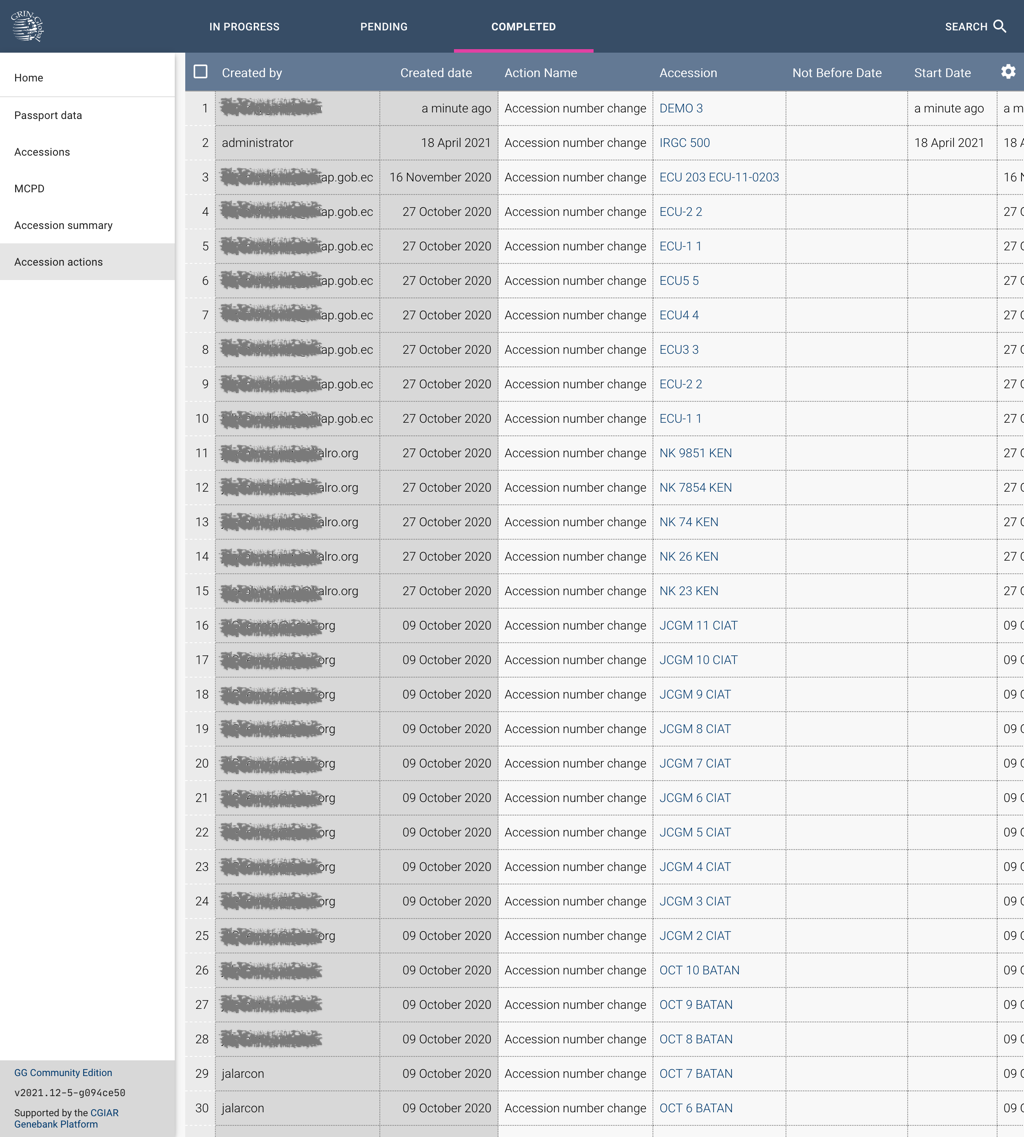
Accessions
This option displays the list of accessions stored in the database, as well as allowing users to add a new accession record.
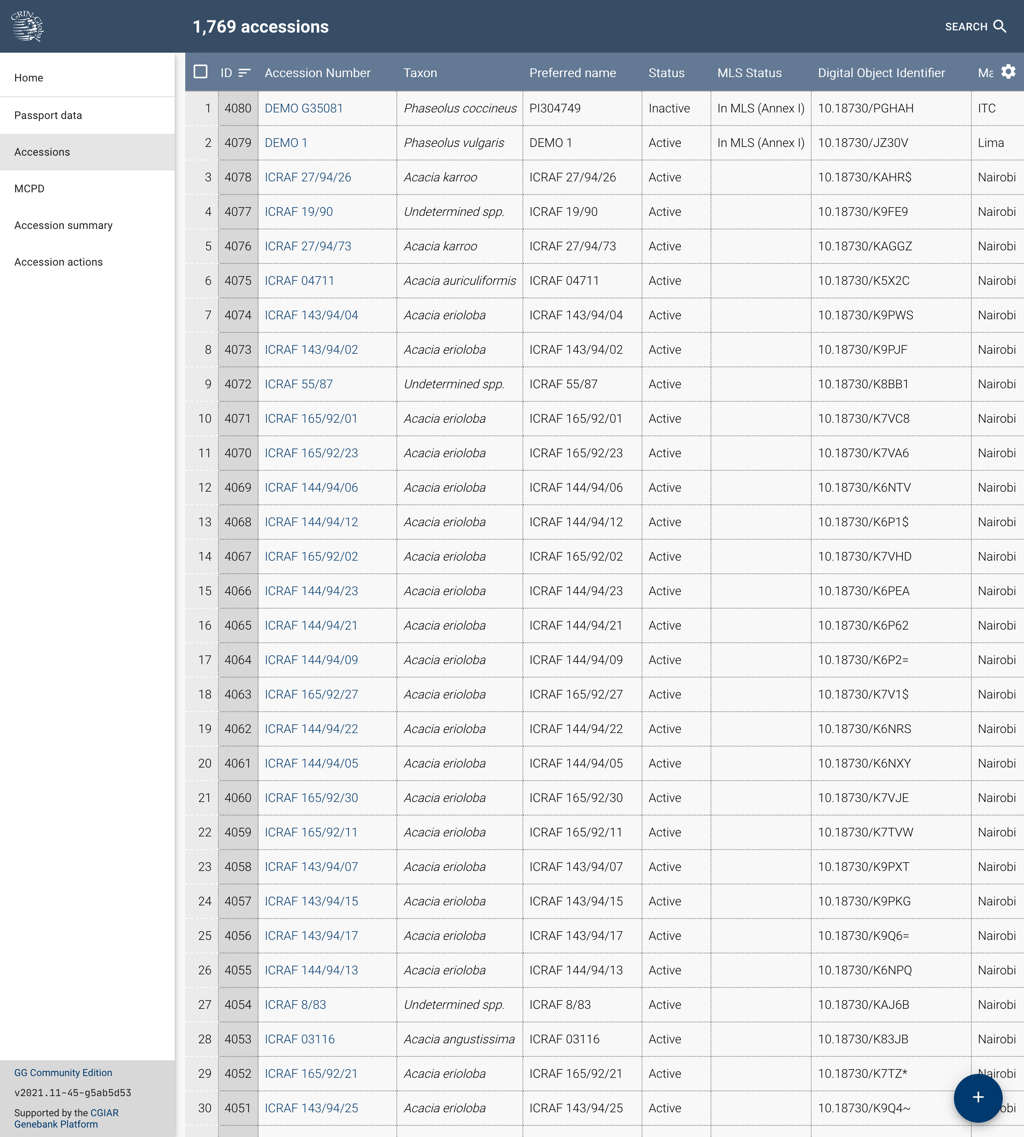
This view collects the primary data regarding accessions in the collection. If you hover the cursor at the end of the column labels you can click on the sort symbol to change the order in which the list is provided.
It is possible to customize the table columns by clicking on the gear ⚙️ symbol in the far right of the table header.
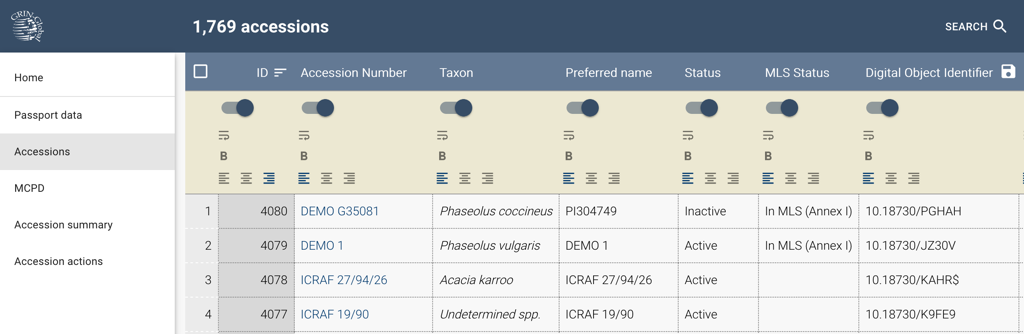
The switch allows you to hide or show the column, wrap the table cell text, set it to bold, and adjust the text alignment.
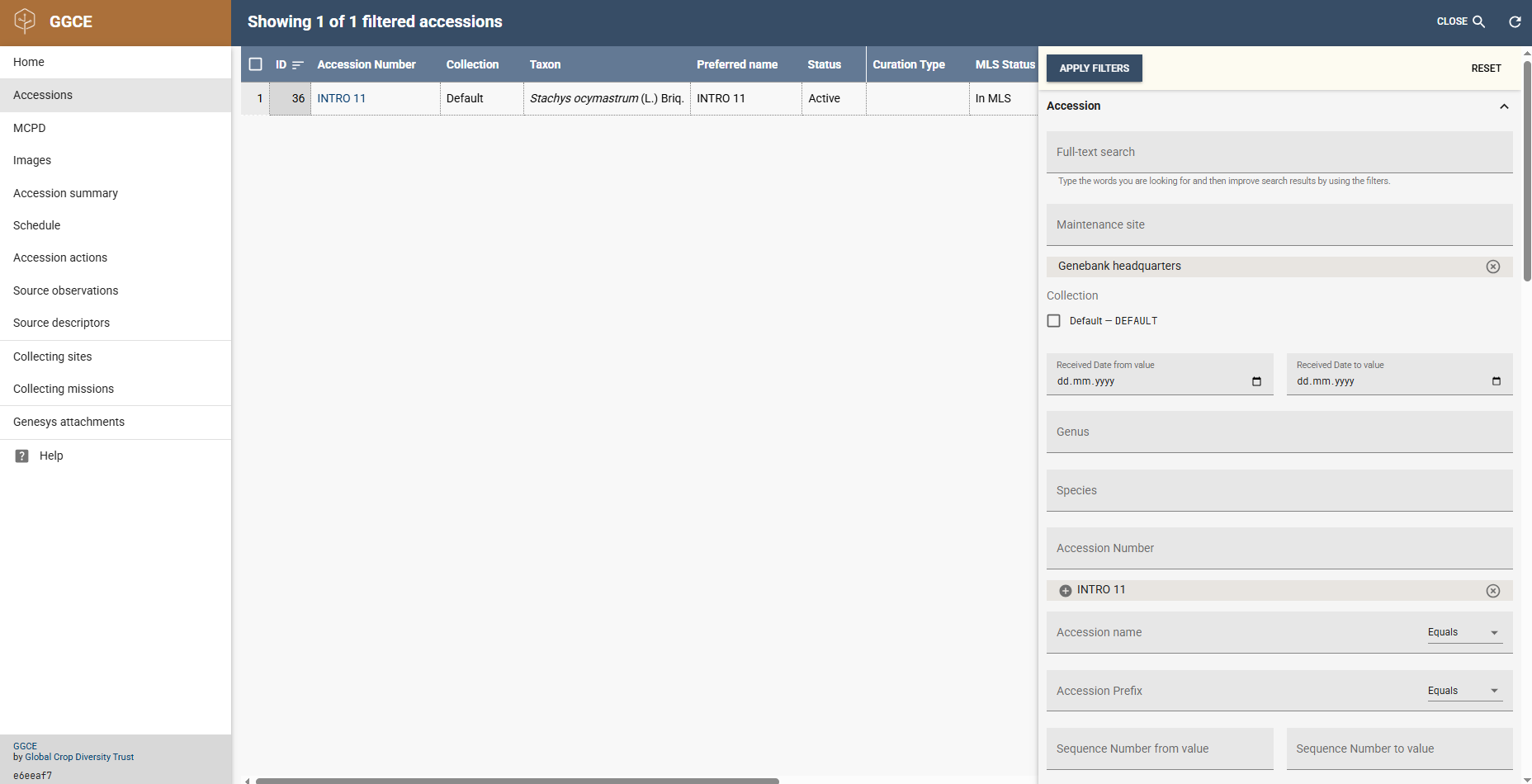
By clicking the SEARCH 🔎 button in the header you can perform detailed queries of the database. After entering the search criteria, click the Apply filters button to retrieve the records matching your query. The search parameters can be reset by clicking the Reset button. Click the Search button again to hide the search panel.
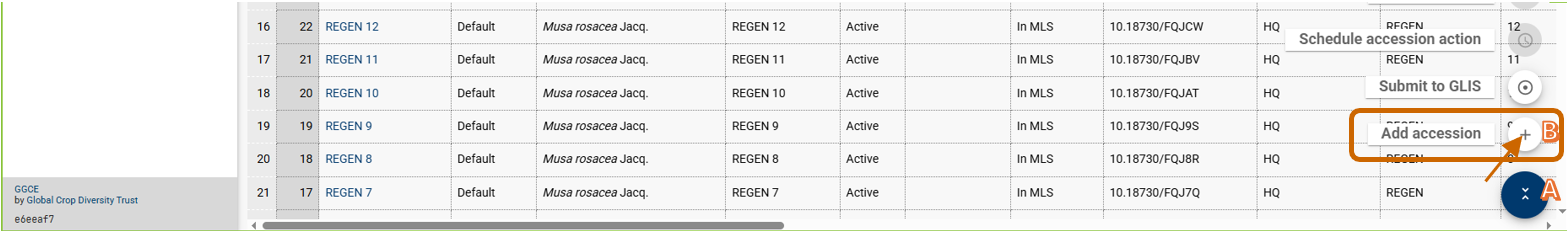
On the bottom right of the accessions list page there is a plus ➕ button that allows you to add a new accession:
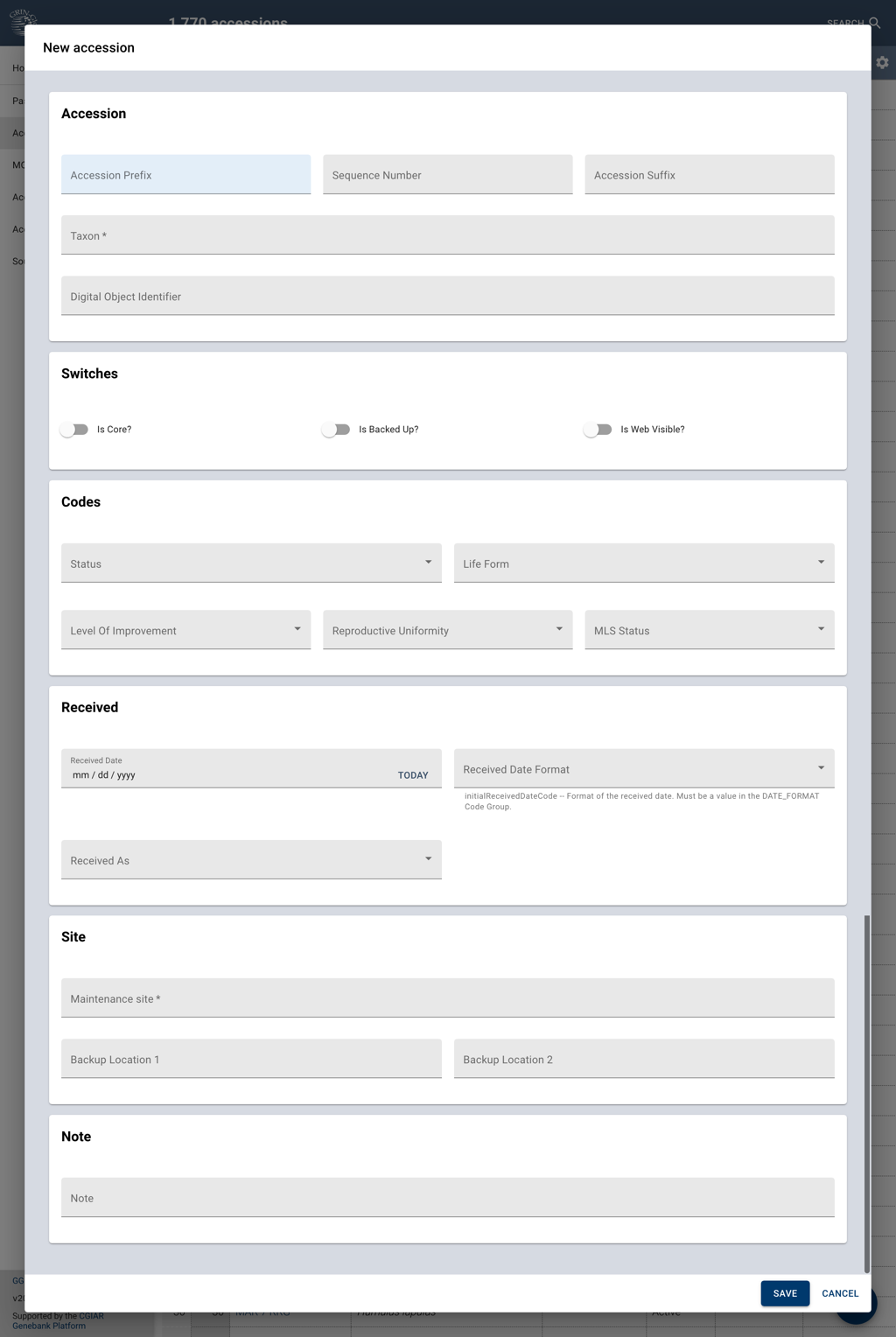
The form groups accession data into several sections collecting related information.
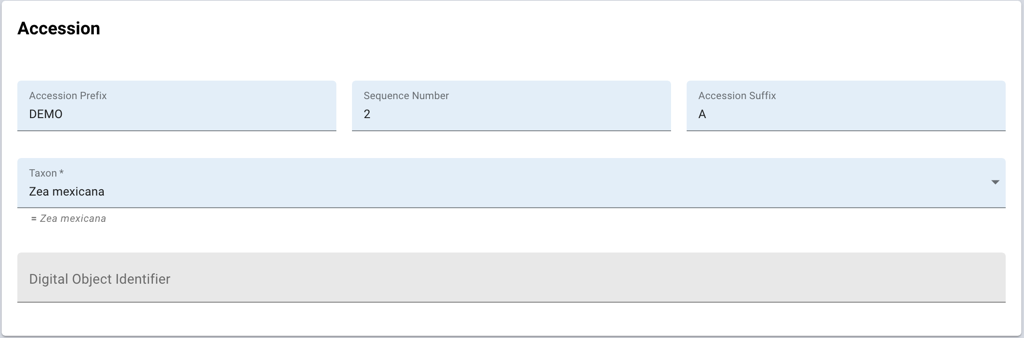
In this section it is possible to set the three components that constitute the accession number (prefix, number and suffix), the scientific name of the germplasm and, if available, the Digital Object Identifier already assigned to the accession in your collection.
Enter the Accession Prefix, if used, the Sequence Number and the Accession Suffix, if applicable. The resulting accession number must be unique within the genebank. The sequence number may be explicitly provided, or, by entering -1, it will be automatically assigned (within the specified prefix) by GGCE.
The Taxon must be selected from a list that is already loaded into the application. GGCE uses GRIN Taxonomy. In the event that the list lacks the desired scientific name, one has two temporary options: if the genus is available one can use <*Genus>* spp., if also the genus is not available, then use Undetermined spp. In the meantime one could ask the curators of GRIN Taxonomy to include the unlisted scientific name and when that has been done, the taxon of this accession can be set to the proper name. The Taxon is required.
The Digital Object Identifier, DOI, is a permanent global unique resource identifier that can be assigned to an accession in your collection. To learn more about DOIs for PGRFA, please consult the website of the Plant Treaty on DOIs.
In this section we can set status switches pertaining to whether the accession is part of the core collection, Is Core, if it is backed up in another genebank, Is Backed Up, and if the passport data associated with the accession can be shared with external users, Is Web Visible.
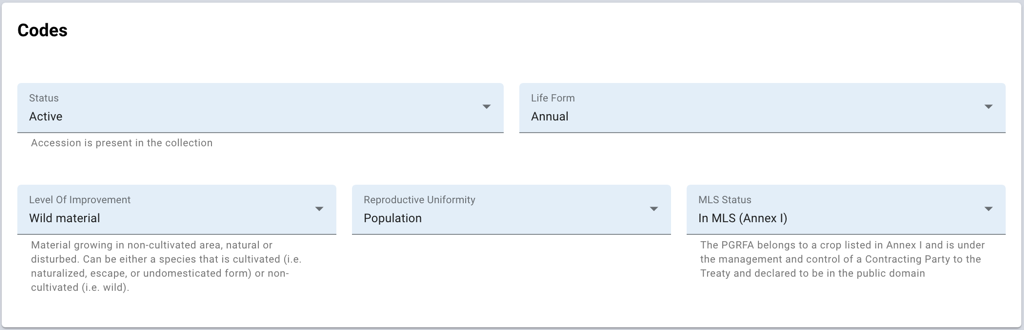
Status indicates what is the accession's status: if it is active, inactive or if it is a security backup. This field is required. We can also specify the accession’s Life Form, which describes the biological form of the material; this information can be customised to suit the needs of the genebank. Level Of Improvement refers to the categories that span from material collected in the wild, to advanced breeding material. Reproductive Uniformity describes the degree of diversity of the sample. Finally, MLS Status refers to how the germplasm stands insofar as the International Treaty on Plant Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture.
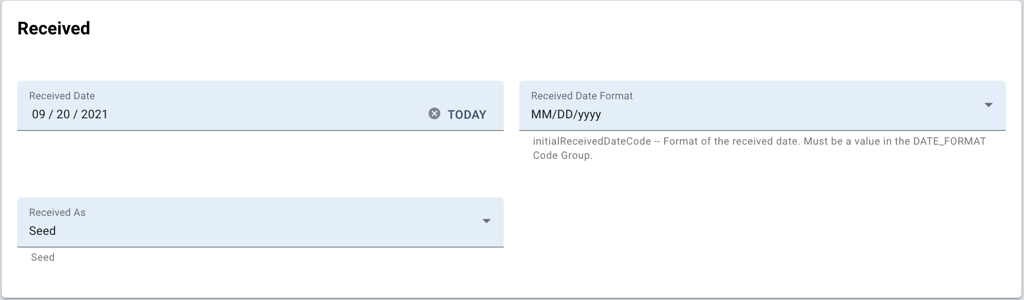
This section records the date at which the germplasm was received and in what form the germplasm was provided, The Received Date Format field is generally used to indicate incomplete date formats: sometimes, especially when recording old data, the day or the day and month may be missing: since the Received Date field is recorded as a date, the Date Format value can be used to ignore day, or day and month.
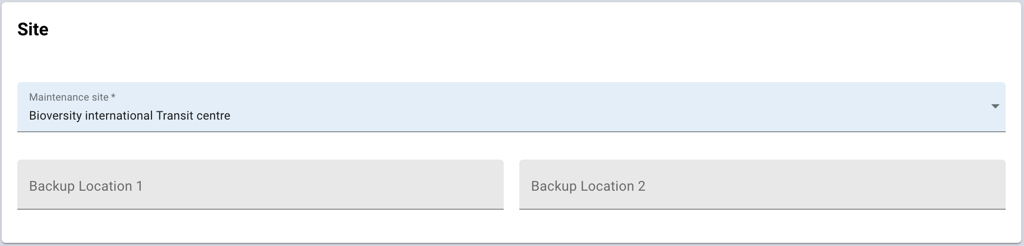
This section indicates which department was assigned the accession and to list the sites in which backup copies of the material are stored.
The Maintenance Site field indicates which division or department of the genebank manages the material and is responsible for updating the passport data. This field is required.
Backup Location 1 and Backup location 2 can be used to record the sites in which backup copies of the accession are stored as safety duplicates.
Note can be used to record internal notes concerning the accession.
Details
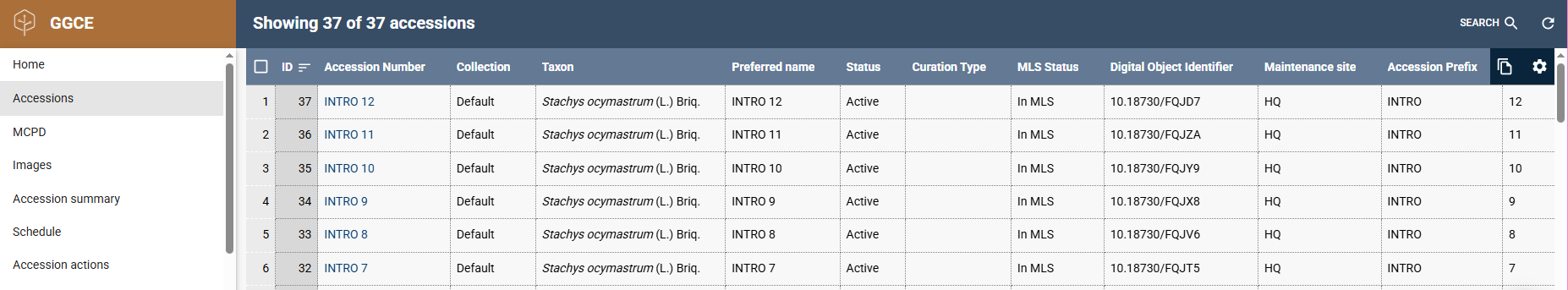
The Accession Number column in the list contains links to accesion details where you can update or delete various aspects of its passport data.
The details page displays a first section with the core data related to the accession, followed by different sections of passport data: Accession names, Accession sources, Accession source cooperators, Intellectual Property Rights/Restrictions (IPR), Accession pedigrees, Accession quarantine and Accession citations.
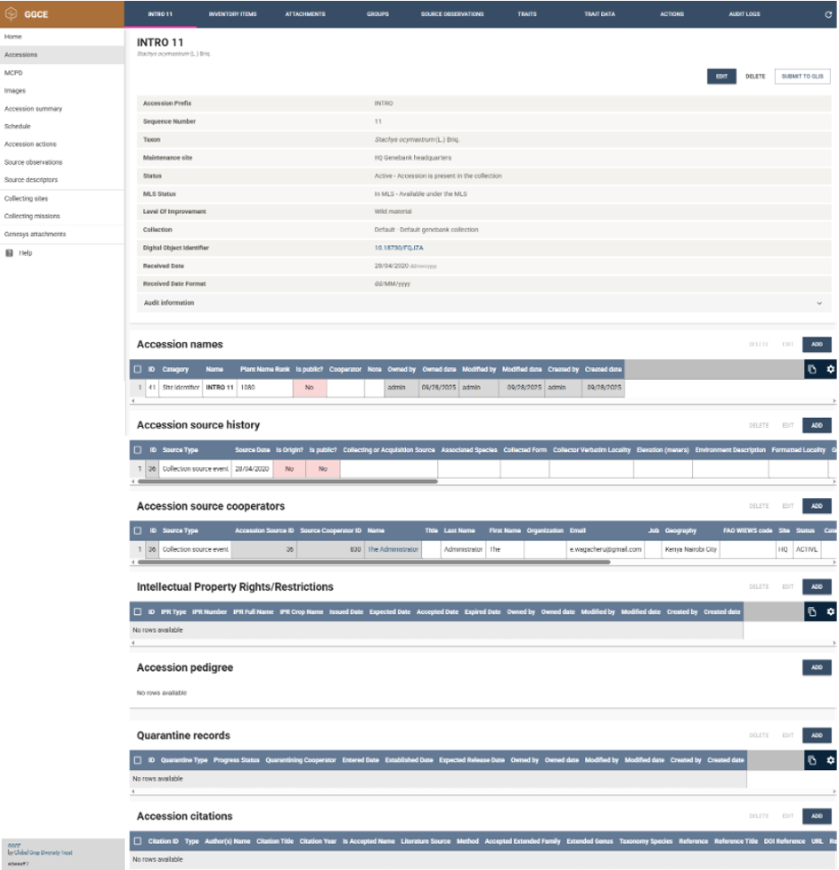
Each section has an ADD button that can be used to add new related records and, by selecting one or more rows, it is possible to add, update and remove individual records. When adding or editing rows, a form is presented with the relevant information.
Accession names
This form can be used to record various germplasm names associated with the accession.
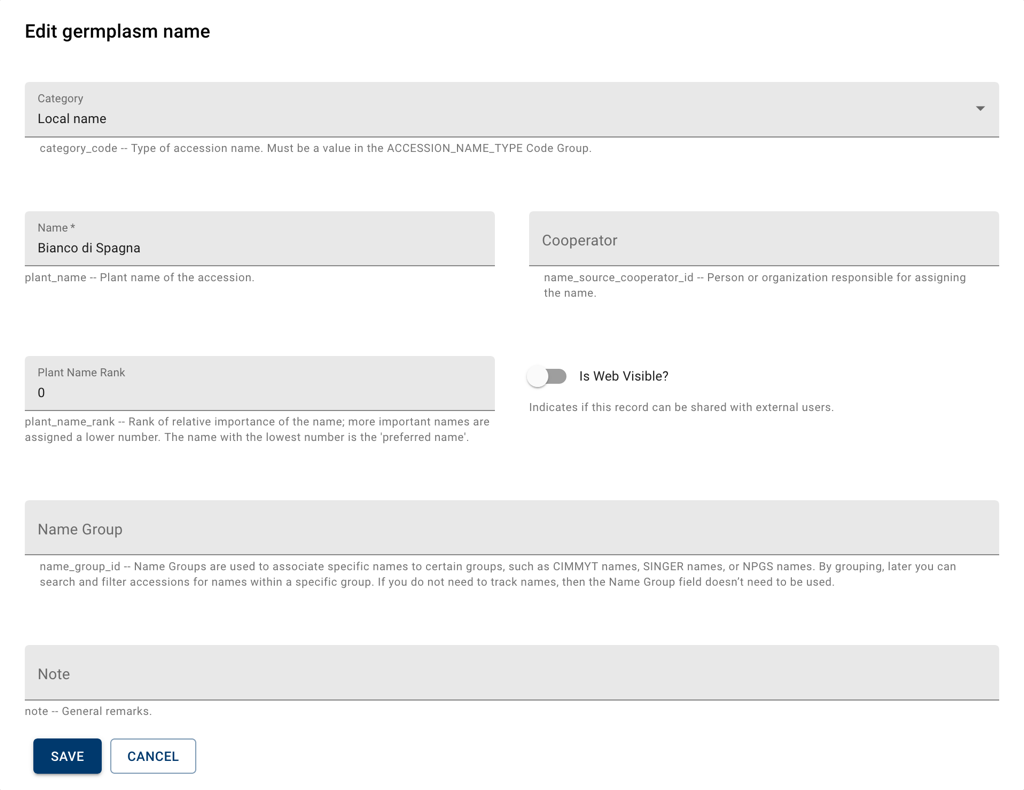
The Category field qualifies the type of the name, this could be a cultivar name, or the identifier of the accession provided by the donor.
The Name field contains the actual text, and is required.
The Name Group is a code, tag or label that can be assigned to the name in order to create name groups or categories.
The Cooperator field can be used to indicate entities connected to the name, such as the donor in donor identifiers.
The Plant Name Rank is an integer value that can be used to rank names: a rank with a lower value will be displayed before a name with a higher rank value, the name with the lowest rank value is considered the default name.
The is Web Visible switch indicates whether the name will be shared with external users.
Accession source history
Accession sources record the significant steps in the history of the accession, from collection or developer source event, throughout the different donor events resulting with the acquisition in the current genebank. The form features the fields related to all three source types, it is clear that, depending on the source type, only a subset of the fields will be relevant.
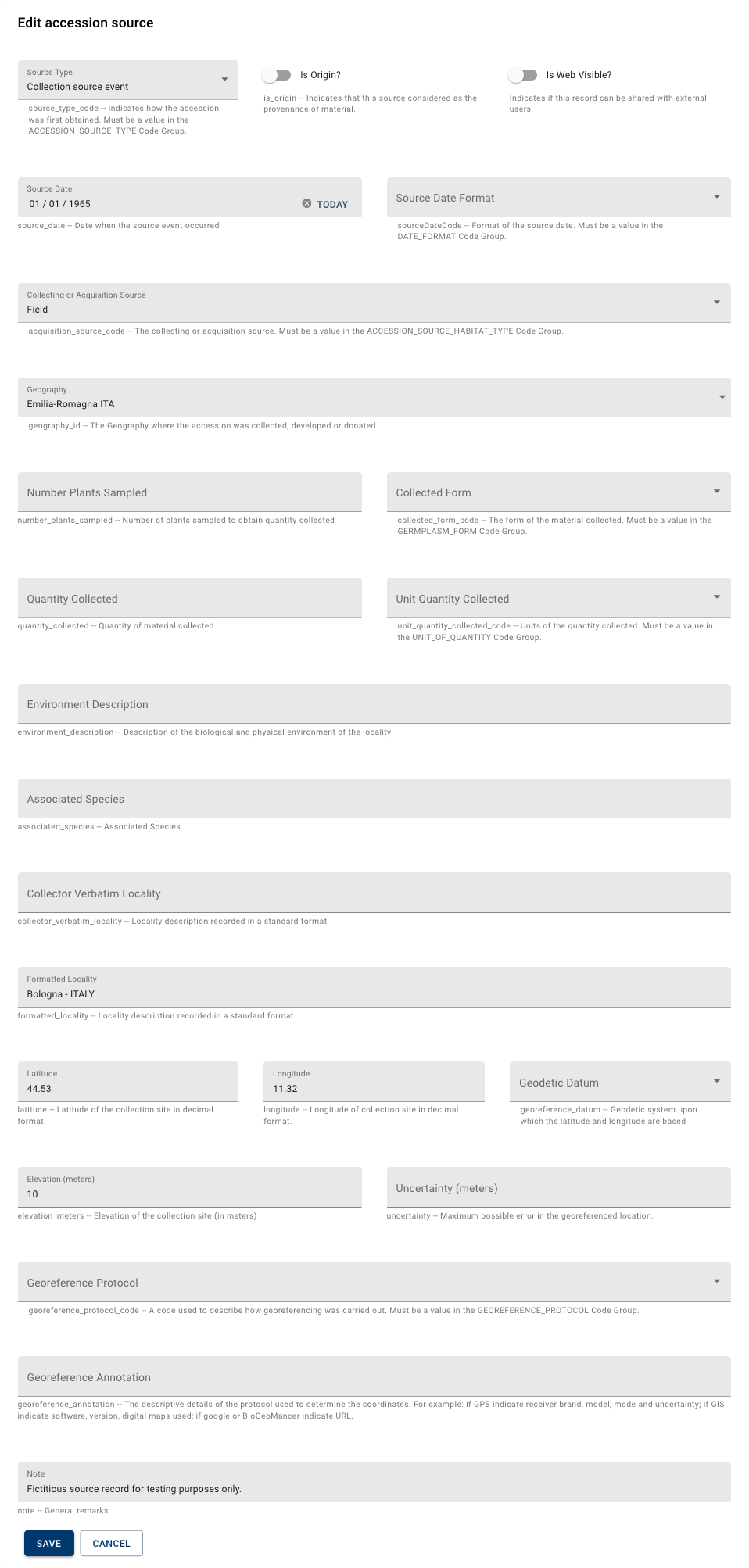
The Source Type indicates what the event relates to. A collecting source event indicates that the form data relates to a collecting mission. A developer source event describes a germplasm obtained by breeding. A donor source event indicates the acquisition of the material from another genebank or entity.
The Is Origin switch is relevant to which source record will be used to fill the MCPD ORIGCTY field, the country in which the sample was originally collected. This also means that the switch should only be set if the source type is a collecting event.
The Is Web Visible switch indicates whether this source record may be shared with external users; this field is relevant to all source types.
The Source Date indicates when the event occurred and the Source Date Format can be used to indicate dates where the day or month and day are missing; these fields are relevant to all source types.
The Collecting or Acquisition Source field is used to describe the sample’s source environment. Most of the choices are relevant to collected material, while Institute and Research station or other ex-situ site could be used in developer or donor source events.
The Geography field can be used to associate the source event to a location expressed as a geographic administrative unit. A set of these records is provided by the application in the Geography table, as new locations are encountered in the data, these can be added to the table. In collecting events it should indicate the original administrative unit in which the collecting mission occurred; it is important to note that one should indicate the administrative unit used at the date of collection. For developer or donor events, this field could indicate the administrative unit of the entity that developed and/or donated the material.
All the next fields, with the exception of Notes, are relevant only to collecting events.
The next group of fields deals with the form and quantity collected. Environment Description should describe in what environment the collecting occurred. Associated Species should list the other species that share, and compete in, the same habitat as the collected sample. Collector Verbatim Locality should record the collecting locality provided by the collector, while the Formatted Locality should contain the locality, cleaned and formatted by the genebank..
The next fields deal with the geographic coordinates of the collecting event. Latitude and Longitude must be provided in decimal degrees format and the Geodetic Datum should be selected according to the coordinates reference frame; WGS 84 is intended for global use. Elevation indicates the location’s altitude relative to sea level (in meters). The Uncertainty field should be used to indicate the coordinate precision (in meters). Georeference Protocol indicates how the coordinate was obtained or determined: if via GPS, with a map or by extrapolating from the name of the collecting site. Georeference Annotation should be used to provide additional details associated with the Georeference Protocol.
Finally, Notes can be used to add any needed comment to the source event.
Accession source cooperators
This section deals with cooperators associated with source history events. Cooperators exist in a dedicated table and are referenced by source event records, cooperator management is covered in a dedicated section of the application.
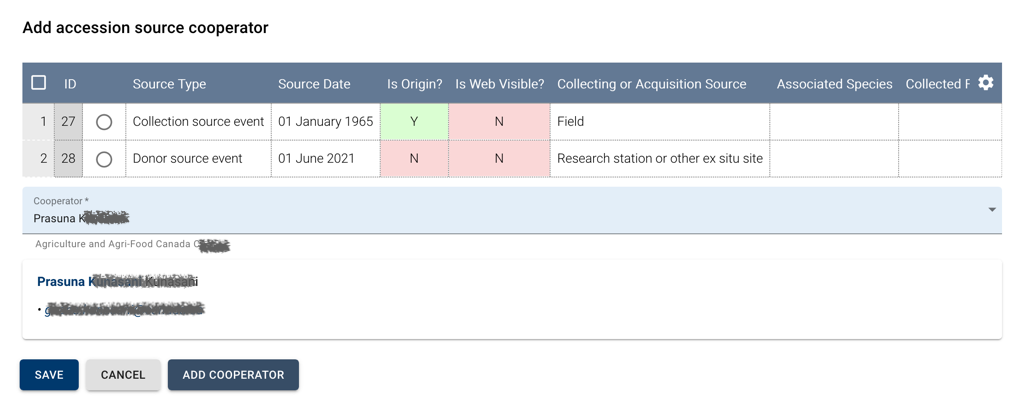
When you press the ADD button a form is opened in which the top part lists the accession’s source events and below there is a field labeled Cooperator. Note the radio button on the right of the ID column in the list must be set on the row corresponding to the source event of interest; when you select a cooperator and press the EDIT button, the radio button will be automatically set to the source event corresponding to the selected source cooperator.
To indicate the cooperator you have two options: select an existing cooperator or create a new one. To select an existing cooperator type its name in the Cooperator field and select an entry from the drop-down list. If the cooperator doesn’t exist yet, you can create it by pressing the ADD COOPERATOR button, you will be presented with a form and once you save the record, you can select it using the Cooperator field.
Note that if you intend to manage cooperators, you should use the dedicated section in the application.
Intellectual property rights/restrictions
IPR refers to registrations, patents or other restrictions associated with the accession; if one or more records are associated with an accession, operations such as distribution will trigger an alert prompting the user to consult these records in order to ensure the operation is allowed.
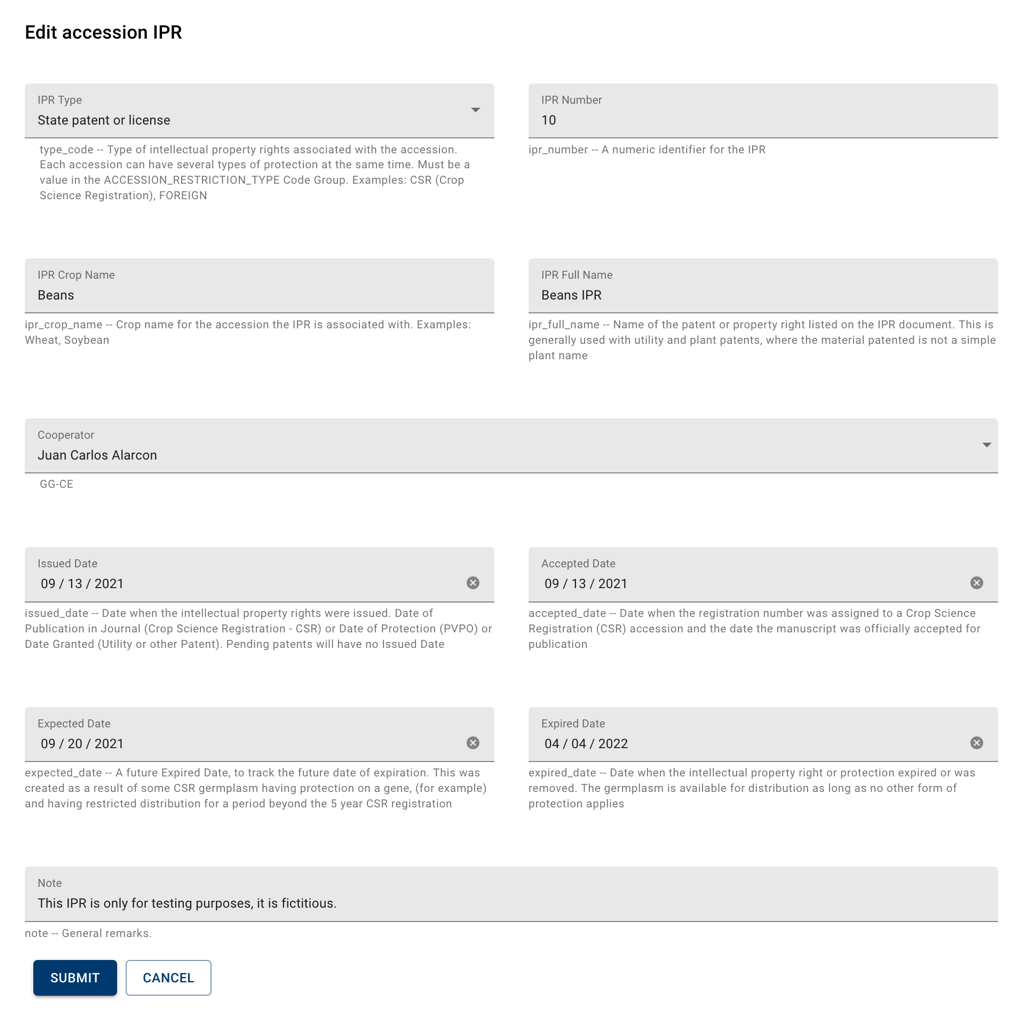
The IPR type field indicates the kind of restriction or registration. The IPR number can be used to record registration numbers. The IPR Crop Name indicates which crop is referenced in the IPR. The IPR Full Name displays the complete registration name. The Cooperator field can be used to record an entity that is responsible or related to the IPR. Issued Date, Accepted Date, Expected Date and Expired Date keep track of milestone dates of the IPR process. Notes can be used to add eventual comments added to the IPR.
Accession pedigree
The accession pedigree is relevant for accessions that are the result of breeding.
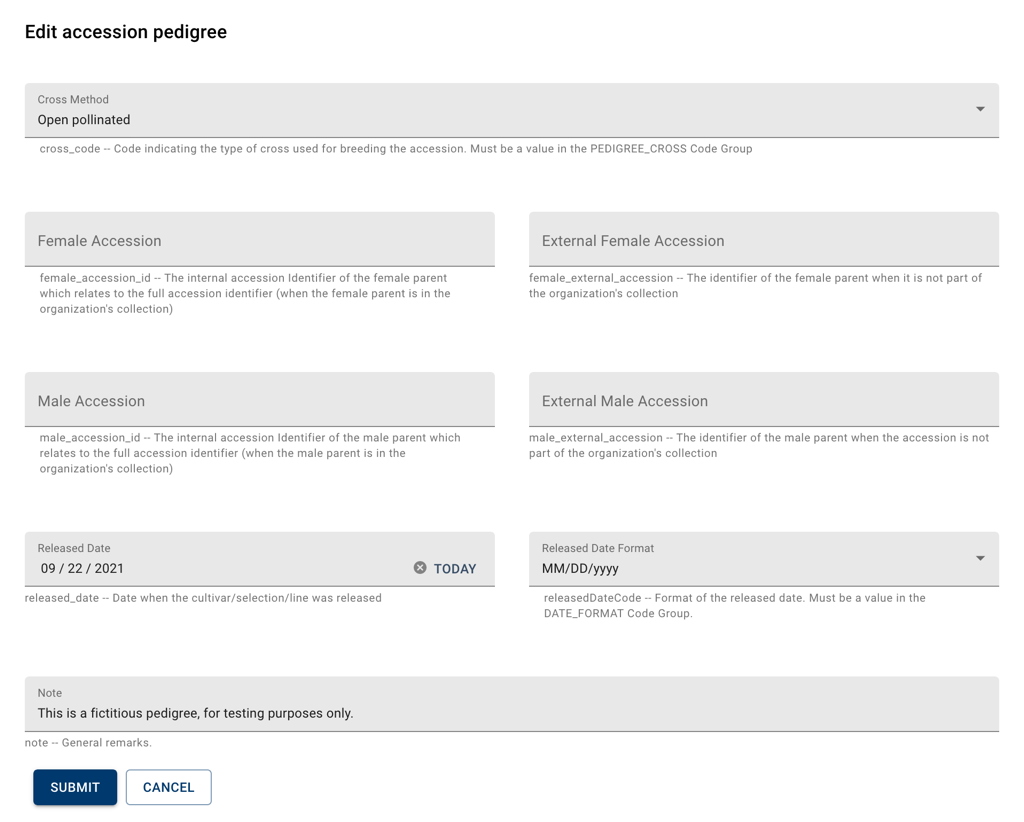
The Cross Method field indicates what procedure was used to obtain the progeny. The four next fields, Female Accession, External Female Accession, Male Accession, External Female Accession, can be used to provide the identifiers of the parents of the germplasm. This information is divided into rows which refer to male and female parents, the left column can be used to insert the identifier of the parent if it belongs to the current genebank and the right column should be used if the parent came from an external source.
The Released Date indicates when the cross was officially released, while the Released Date Format field can be used to indicate missing day, or month and day.
Notes can be used to add additional information.
Quarantine records
Accession quarantine allow for tracking the progress of an accession as it goes through a quarantine process.
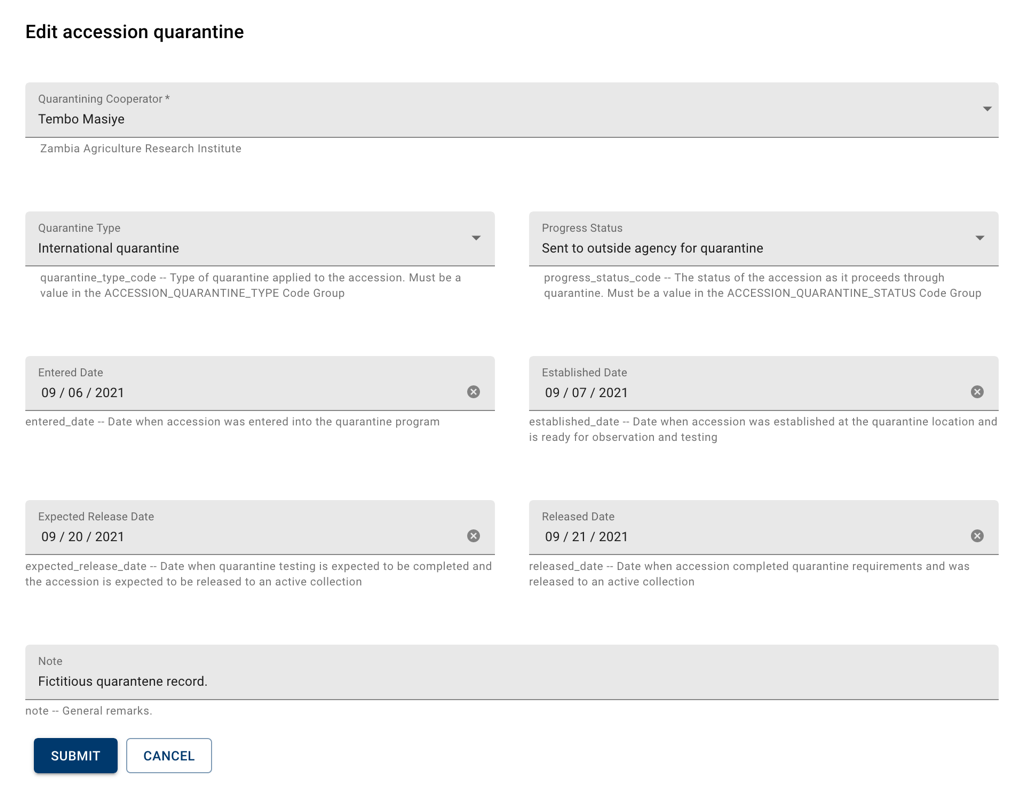
The Quarantining Cooperator field can be used to indicate the person or entity responsible for the process.
The Quarantine Type field indicates the specific quarantine procedure the accession went through and the Progress Status field indicates the status or outcome of the process.
The four following date fields, Entered Date, Established Date, Expected Release Date and Released Date, can be used to document when the accession entered the quarantine program, when it was established at the processing location, when the procedure was expected to be completed and when the accession was released.
The Note field can be used to add further details.
Cooperator and type are required fields.
Linked data
The header of the accession details page features the accession number as the first element on the left, the other elements are menu buttons that provide access to other data linked with the accession.
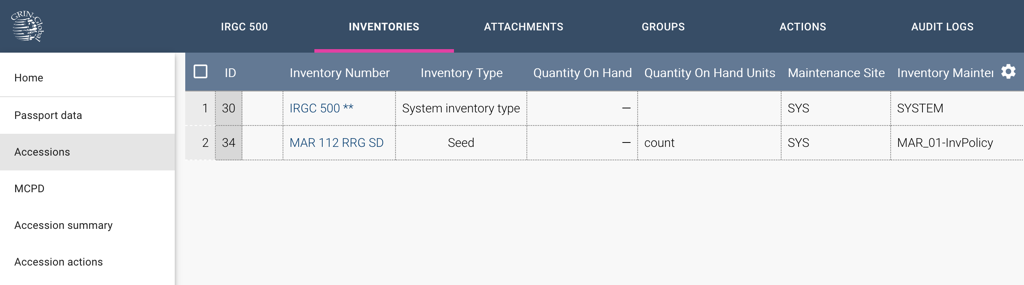
Inventories
Inventories displays the inventory of germplasm of the accession. Clicking any Inventory Number will display the details of the selected accession inventory item. The list is read-only.
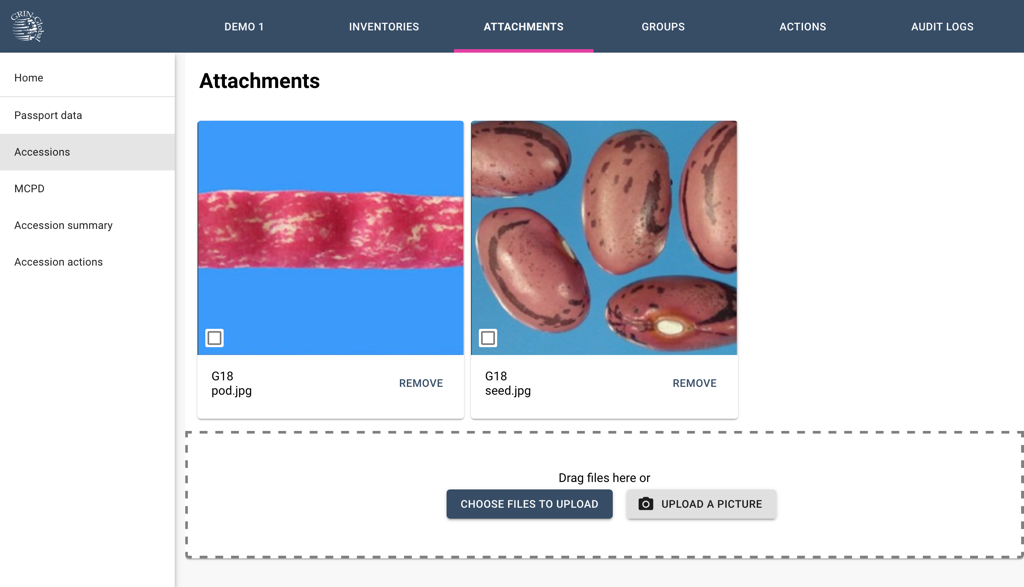
Attachments
Attachments are used to view and add documents and images related to the accession.
Groups
Groups lists all the groups to which the accession belongs. The management of groups and members of groups is discussed in Inventory Groups.
Audit logs
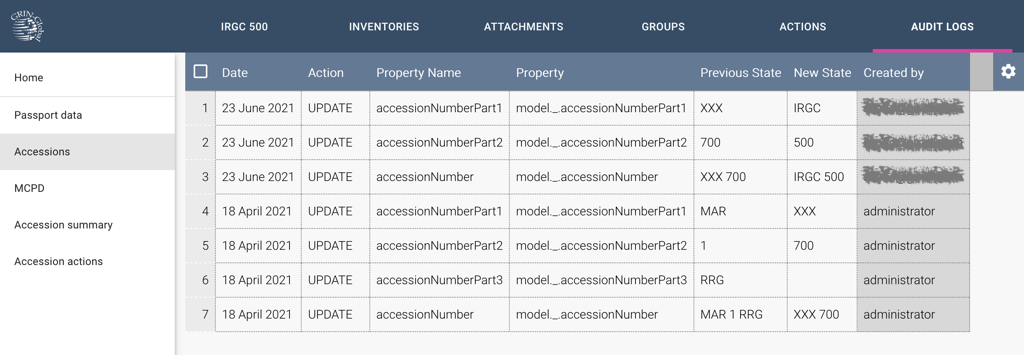
Audit logs display database-level changes made to the accession data, which field was involved, the previous and the updated value, who made these changes and when.
Accession summary
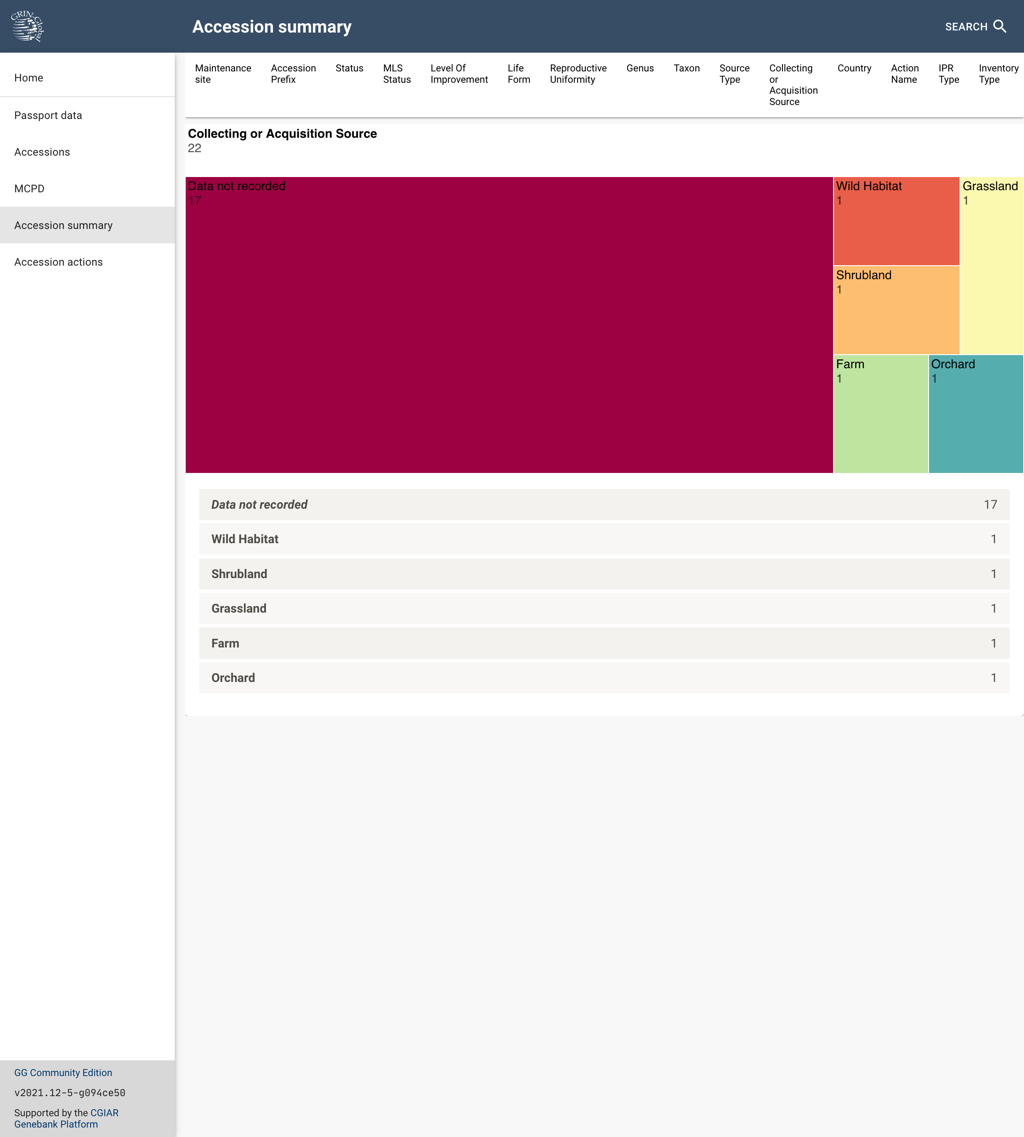
Accession summary displays a chart that groups accessions according to a list of data elements that are displayed below the page header. When you click on one of the fields, accessions will be grouped according to the values of that field and the graph will change according to the matching records count, as well as displaying the details in the rows below the graph.
Accession actions
In Accession actions you can browse accession-level actions that are in progress, pending, completed or are scheduled in the future.